The hydraulic pump is the core power element of the hydraulic system, responsible for converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, thereby providing the required pressure and flow for the hydraulic system. There are many types of hydraulic pumps, which can generally be divided into gear pumps, plunger pumps, vane pumps and screw pumps.
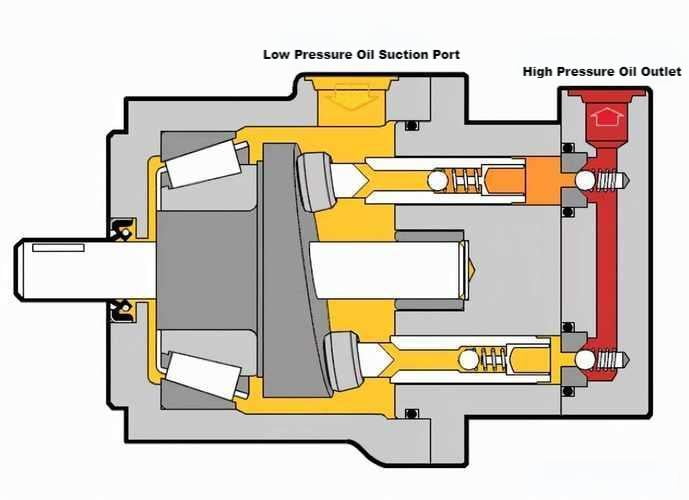
Working principle of hydraulic pump
The working principle of the hydraulic pump is to periodically change the volume of the working chamber in the pump through the movement of the working element, thereby completing the process of oil suction and oil pressure. Different types of hydraulic pumps have different characteristics and applicable scopes, and need to be selected according to specific application scenarios.
- Oil suction process:
- When the hydraulic pump starts working, the working elements such as gears, plungers or blades in the pump start to rotate or reciprocate.
- As the working elements move, the volume of the working chamber in the pump gradually increases, forming a low-pressure area.
- Due to the pressure difference, the oil in the oil tank is sucked into the working chamber in the pump.
- Oil compression process:
- As the working element continues to move, the volume of the working chamber in the pump gradually decreases.
- Due to the decrease in volume, the oil in the working chamber is squeezed and the pressure gradually increases.
- The high-pressure oil is discharged through the oil outlet of the pump and transported to the pipeline of the hydraulic system.
- Flow distribution action:
- In the process of oil suction and oil compression, the hydraulic pump needs to complete the flow distribution action, that is, to ensure that low-pressure oil is sucked in when the volume increases, and high-pressure oil is discharged when the volume decreases.
- This is usually achieved through components such as the distribution plate, oil distribution plate or one-way valve in the pump.
- Sealing and leakage control:
- The hydraulic pump needs to remain sealed during operation to prevent oil leakage.
- Sealing is usually achieved through sealing components (such as sealing rings, gaskets, etc.).
- Leakage control is an important factor to be considered in hydraulic pump design, because leakage will affect the performance and efficiency of the pump.
Features of different types of hydraulic pumps
- Gear pump: simple structure, easy maintenance, suitable for low-pressure systems. But it is easy to generate vibration and noise, and has large leakage.
- Vane pump: high working pressure, small flow, stable operation, suitable for medium-pressure systems. But it is sensitive to oil contamination.
- Piston pump: high working pressure, adjustable flow, suitable for high-pressure systems. But the structure is complex and the cost is high.
- Screw pump: simple structure, strong self-priming performance, strong adaptability, but sensitive to temperature and high cost.



