Hydraulic pump is a common pump in engineering. It converts the motor’s energy into liquid pressure to provide pressure for the hydraulic system. Six types of hydraulic pumps include gear, vane, piston, screw, and magnetic pumps. They vary in power and structure.
Gear pump:
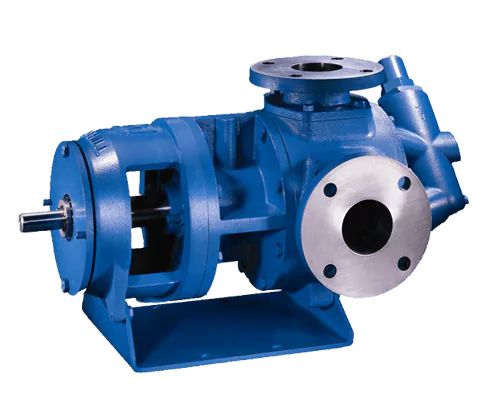

People commonly use the gear pump in hydraulic systems. It has a simple design, low cost to make, high flow rate, and steady pressure.
Application scenario: Suitable for conveying liquids with low temperature, such as water, hydraulic oil, etc.
Advantages and disadvantages: compact dimensions, simple layout, and cost-effective rate. However, the oil cleanliness requirements are not strict. One drawback is that the pump shaft is prone to unbalanced force, leading to wear and leakage.
Vane pump:
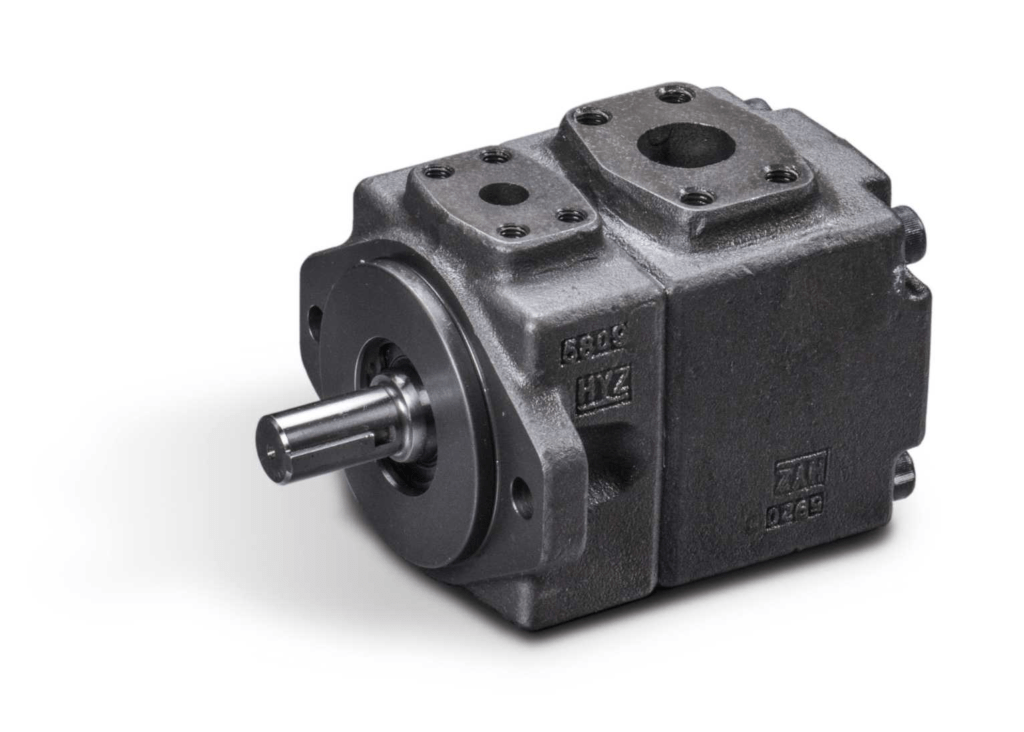
Features: Compared with gear pumps, vane pumps have higher flow and pressure. The main structure consists of rotor, stator, and blade.
This pump operates effectively in high-speed and high-pressure situations. Perfect for creating hydraulic high-pressure systems in manufacturing.
Advantages and disadvantages: Consistent flow, seamless functioning, minimal sound. Working pressure and volumetric efficiency are higher than gear pumps, but the structure is more complex.
Plunger pump:
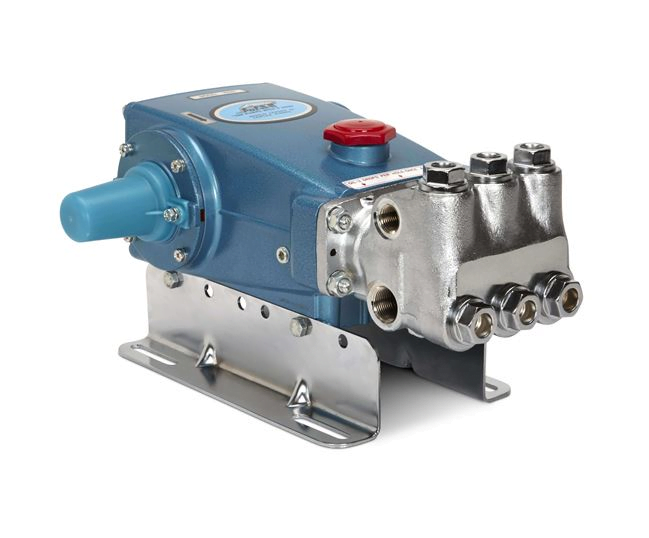

Features: The plunger moves back and forth to move liquid with high pressure, large flow, good sealing, and other benefits.
Application scenario: Suitable for high pressure and large flow hydraulic system.
Advantages and disadvantages: effective with large quantities, negligible leakage, capable of managing high pressure. However, complex structure, requires high material and processing accuracy, expensive, and requires high oil cleanliness.
Piston pump:
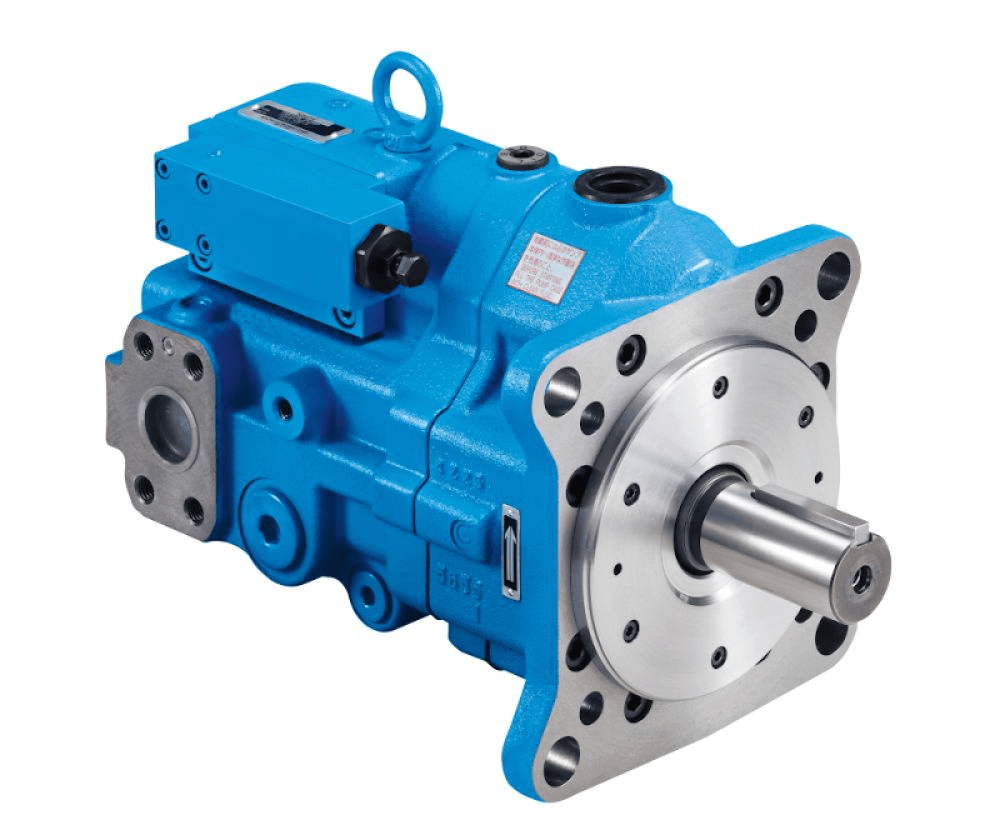
The features include a structure similar to a plunger pump, but with a piston as the plunger.
Application scenario: This parameter is applicable to specific scenarios, such as scenarios where traffic is adjustable.
Pros and cons: You can adjust the flow rate, but the pressure is a bit lower compared to the plunger pump.
Screw pump:
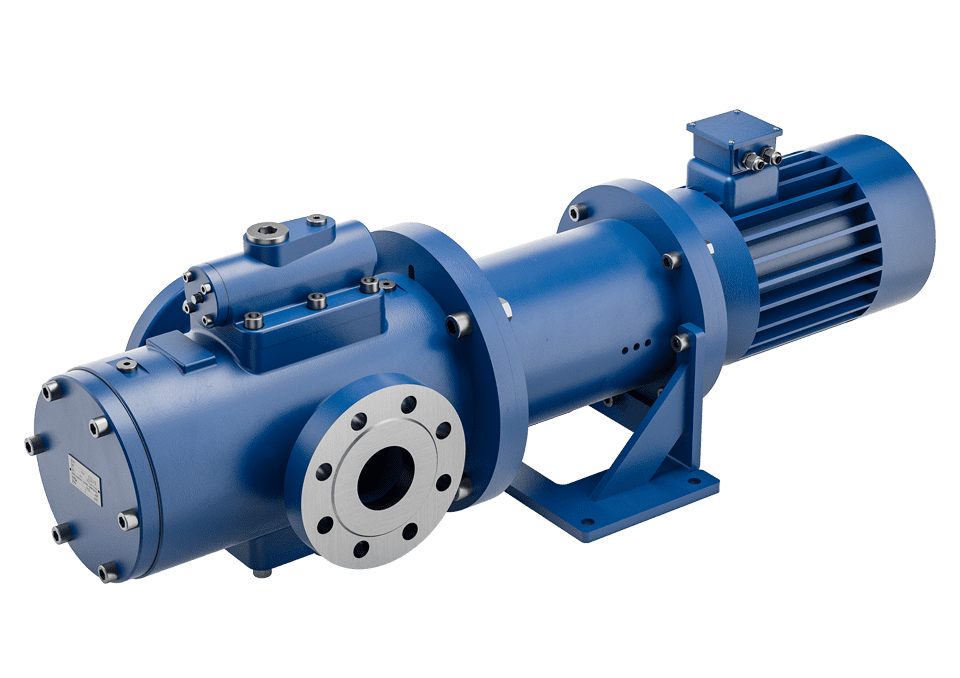
Features: The main structure is the stator and rotor, through the rotation of the screw to achieve liquid transportation.
Application scenario: It is suitable for conveying liquid with high viscosity, such as paste.
Pros and cons: Can handle high viscosity liquids, but may not work with all hydraulic systems.
Magnetic pump:
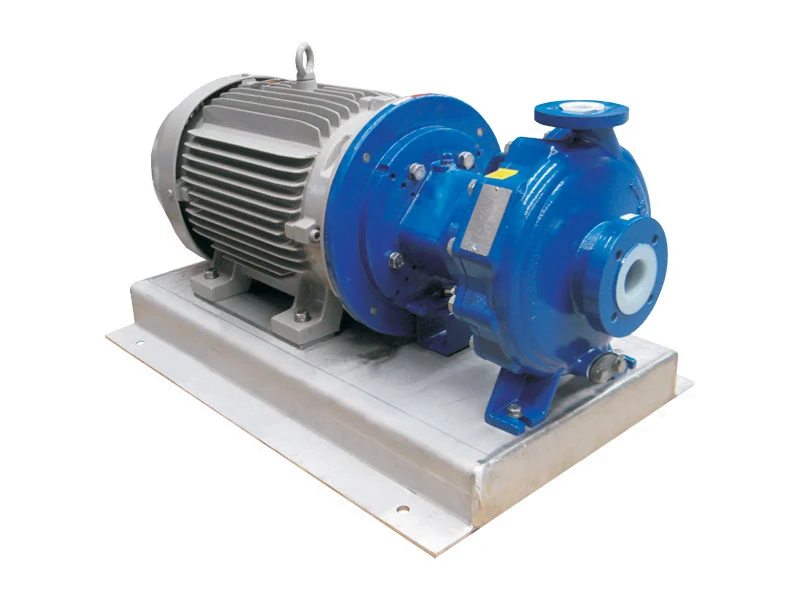

Features: Magnetic pump is a liquid transfer pump that operates through a magnetic drive impeller without mechanical seal.
Application scenario: Mainly suitable for transporting corrosive liquid and flammable and explosive liquid.
Advantages and disadvantages exist. No need for a mechanical seal reduces the chance of leaks. However, limitations may exist in efficiency and material choices.
Users can choose different types of hydraulic pumps according to the use scenario and characteristics.



